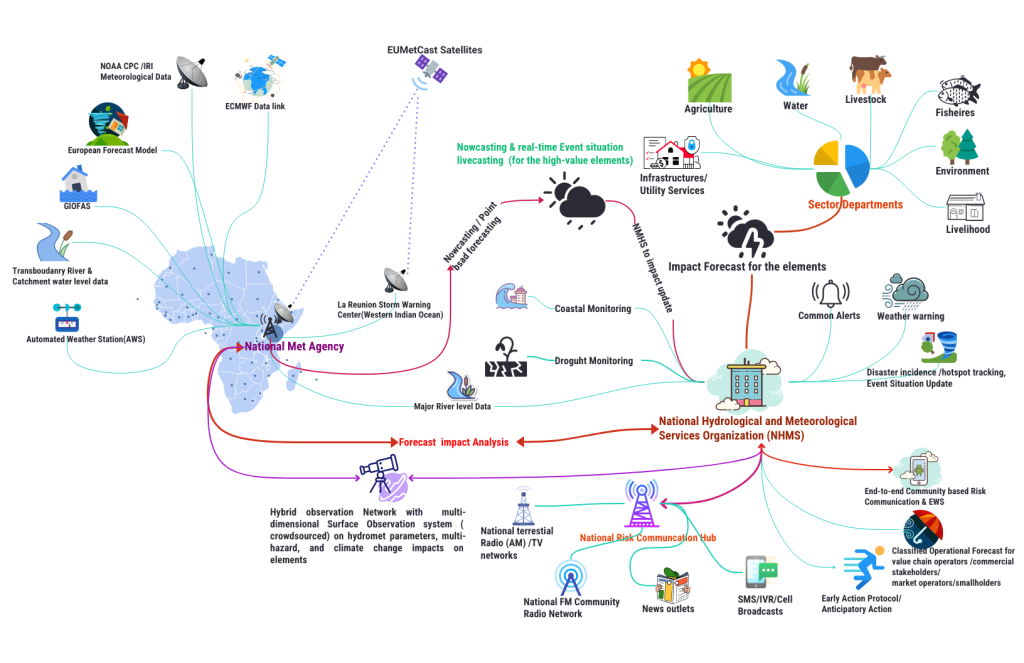
The Multi-hazard Early Warning System Design & Implementation Center (MHEWC) provides technical support at the country level to design, install, and operationalize the ICT Integrated National Multi-Hazard Early Warning Center (NMHEWC).
NMHEWC sounds big, but we’ve just begun our journey… We support for new installation, diagnose the existing system operational capacity and support for upgrading the country-level NMHEWC integrated system essentially be functional as an interoperable and integrated ICT online database system, geospatial platform (automated standard alerting system, web-based database & apps based interface ) with interconnectedness of all relevant climate-vulnerable sector departments, diverse stakeholders, value chain operators, and frontline vulnerable communities to interact with an integrated system.
The NMHEWC system can support weather impact forecasting, operational forecasting, common alerting, event situation updates, and generate classified alerts for elements. The integrated NMHEWC aims to promote a digital (online) local risk management governance system that overcomes institutional coordination barriers in risk assessment, risk repository development, and data exchange mechanisms across all administrative levels of local governments, and extensively covers last-mile, multi-stakeholder-led risk governance management.
Typical & simplified MHEWS design for African Countries
Designed & conceptualized by Z M Sajjadul Islam ( for any comments and updates, please contact )