National Emergency Crisis and Disasters Management Authority (NCEMA)
The establishment of NCEMA was announced on May 14, 2007 within the organizational structure of the Supervision of the Supreme Council for National Security and based on a decree by Federal Law No. (2) for the year 2011. The announcement reflects the wise leadership’s keenness on ensuring the safety of the lives of all citizens and residents on the territory of the United Arab Emirates and to preserve the property of the country.
NCEMA operates under the Supervision of the Supreme Council for National Security, with the aim to achieve the UAE’s policy regarding the necessary procedures for emergency, crises and disasters management. It’s the major national standard-setting body responsible for regulating and coordinating all efforts of emergency, crisis and disaster management as well as the development of a national plan for responding to emergencies. Therefore, its work is focused mainly in the development, consolidation and maintenance of laws, policies and procedures of emergency and crisis management at the national level.
NCEMA oversees the development of response capabilities by proposing and coordinating programs among stakeholders at the local and national levels, and updating them on a regular basis. In addition, it participates in preparing the risks and threats log at both national and local levels, and periodically updates it in cooperation and coordination with the concerned authorities.
NCEMA also coordinates the roles of the concerned governmental parties in the event of an emergency, crisis or disaster. It engages in the preparation and coordination of the essential emergency plans for vital facilities and infrastructure, and following up on their implementation in coordination with the concerned governmental authorities.
NCEMA conducts the necessary studies and researches through a dedicated center for information and resources related to predicting emergency, crises and disasters and how to deal with them in coordination with the concerned authorities. Moreover, it prepares, coordinates, and implements the exercises related to emergency, crises and disasters management in coordination with the concerned authorities and follows up on their implementation.
About NCEMA
- Vision
- Mission
- Values
- Strategic Objectives
- NCEMA in Focus
- Vice President Message
- Departments
- Laws and Legislation
Strategic Objectives
The ability to achieve Security and resilience.
- Ensuring the quality of life through the implementation of premier public safety standard.
- Enriching the readiness and national communication and cooperation within the Emergency, crisis and disaster management communitsy.
- Optimization of advanced technolog.
- Development of corporate resources and innovation.
Open Data
World Disaster Statistics
Electronic Decision Making
Introduction
The UAE government gives high priority to the engagement of and continuous communication with customers to make decisions and improve the services offered to them. Hence, the National Emergency, Crisis and Disaster Authority (NCEMA) seeks to engage as many customers as possible and take their opinions via
online questionnaire which will be analyzed and used in making decisions that would be useful and enhance satisfaction of the customers.
The National Early Warning System
The National Early Warning System (EWS) is a set of procedures, policies and technologies, together, focus on the wellbeing and safety of all residents in the UAE, including the visitors. This is achieved through effective and fast public warning. The importance of EWS lies in the following main objectives:
Preserve lives and property by reducing the impact of emergency crises and disasters, by reaching as many people as possible to warn them of the potential danger or threat through various means of disseminations in a timely manner.
The governance of the EWS throughout the country and all the government agencies and institutions in the UAE for the proper coordination in the process of warning and dissemination and to ensure the effectiveness of public response and interaction.
Ensure the accuracy and speed of issuance of warnings through the activation of integrated electronic systems.
Supporting the emergency management system in the UAE in all the phases of an emergency.
Strengthening the status of the UAE and its classification in the global indicators of readiness.
Participate
The Ncema App
The app of the National Emergency, Crisis and Disaster Management Authority is a mini-system to present all services provided by the Authority. The browser can identify the awareness guide, in addition to warning messages and evacuation centers, along with the initiatives of NCEMA such as the national volunteer program.
The app also includes additional information about the Authority, such as the history of creation, the media center, and the digital versions produced by the NCEMA.
Participate
Awareness Series to Emergencies Crises and Disasters
First Edition: Dealing with Tremors and Earthquakes
Tremors and earthquakes are among the most dangerous natural disasters in terms of their devastating effects on human lives, individual properties and country infrastructure.
They occur so suddenly, leaving governments and individuals barely any time to protect themselves. Their consequences and reach are difficult to predict; they cannot be controlled nor can their intensity or the damage they cause be minimised. For these reasons, countries and governments seek to develop awareness programmes, measures and instructional campaigns that aim to instil a culture of safety within the community.
In this context, NCEMA has launched a major awareness initiative under the directives of the country’s wise leadership. It aims to instil a culture of prevention and safety by providing the community – nationals and residents alike – with the knowledge that enables them to sensibly and responsibly deal with natural disasters of different types and intensities. For that purpose, NCEMA employs all available methods and communication technologies to reach out to the population at large.
Dealing with Tremors and Earthquakes shows you the best ways to protect yourselves and those around you, to ward off any unforeseen dangers, to act sensibly and wisely in any case of emergency and to avoid any erroneous practices likely to lead to unfortunate consequences.
Second Edition: Responding to Weather Flutuations and Bad Weather
Weather fluctuations: It is a state of atmospheric instability in a particular area and the associated spread of dark clouds and formation of heavy fog, wind, thunderstorms, lightning, heavy rainfall, hails and possibly snowfall due to the impact of a depression on the surface of the earth. Natural disasters are still difficult to predict by humans in terms of accurate knowledge of the time, place and impacts; however, specialized studies and research have made great strides in the development of plans, programs and procedures to reduce the hazards of these disasters, both at the level of human losses or material damage.
This guide comes in the context of a series of guidelines and manuals the National Emergency, Crisis and Disaster Management Authority is aiming to generate in the context of its awareness plan. This plan is aimed at laying the foundations of public safety culture in the community and creating a comprehensive awareness among institutions and individuals on how to deal with disasters and risks with sufficient awareness and responsibility to preserve their lives and the environment in which they live along with all its contents and components.
Participate
National Volunteers Program
Vision
“Forming a distinguished base of volunteers in the field of emergency, crises and disasters”.
Mission
“Qualifying the State volunteer leaders with the view of supporting the efforts of national response during emergencies, crises and disasters to preserve lives and sustain the State’s achievements”..
Objectives
Attracting individuals of the community who are interested to volunteer and encouraging them to effectively assist in social development.
Establishing, qualifying and training a team of volunteers that will contribute to the assistance during emergencies, crises and disasters.
Establishing a database of volunteers to coordinate their work within the efforts of the national response.
Supporting programs specialized in the management of the National Career Level to guarantee the continuity of work during emergencies, crises and disasters.
Instilling and promoting the culture of volunteerism within the society.
Strengthening the sense of belonging, and social cohesion between community members and the State authorities, and collaborating during emergencies, crises and disasters.
Participate
Your Emergency Guide
Questionnaire Subject
Your Emergency Guide is a guide issued by NCEMA to reduce risks that may happen to the citizen and resident in order to protect people and property as well.
NCEMA is keen to explain all the correct procedures to be followed in the case of emergency, crisis or disaster at work or at home with family members.
Your Emergency Guide provides guidance to save lives and property and create a society that is able to deal with emergencies, crises and disasters for a safe and happy society.
NCEMA has directed several questions to customers via a questionnaire to ensure that Your Emergency Guide has been delivered. Through the questionnaire, the customer opinions will be surveyed to improve the methods of delivery of the guide to as many customers as possible.
Questionnaire Objective
Improve and develop the methods of delivery of “Your Emergency Guide” to customers.
Decision Making
NCEMA will seek to improve the ways to communicate the guide to as many people as possible and implement the proposals made.
Participate
Awareness and Education via NCEMA Official Website
Questionnaire Subject
As NCEMA believes that awareness and education is very important to improve the culture and awareness of the public about the correct procedures to be taken (before, during, after) emergencies, crises and disasters as listed on NCEMA website (available also via NCEMA application) in relation to emergencies, crises and natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, sand storms in addition to dense fog and epidemics such as Coronavirus. NCEMA raise awareness via a variety public awareness threads at the NCEMA official accounts on the social media.
NCEMA aims to raise awareness and promote the emergency, crisis and disaster culture and explain how to deal with all emergencies, crises and disasters in a quick and correct way to save lives and property
In this questionnaire, NCEMA asks several questions to ensure that the awareness messages are conveyed to the customers. The questionnaire will also survey the public opinion on how to improve methods used to promote emergency, crisis and disaster culture among members of the society.
Questionnaire Objective
To improve and develop methods used to promote awareness among the public and instill the ECD culture in the society.
Decision Making
The ideas and opinions will be analyzed and monitored and based on this, new ways will be adopted and added to promote the emergency and crisis culture in the society.
Participate
Emergency and Crisis Magazine
Questionnaire Subject
NCEMA publications include Emergency and Crisis quarterly magazine that discusses a variety of topics including ECD studies and research. It also includes interviews with prominent figures who have extensive experience in the ECD area at local or international levels.
Emergency and Crisis Magazine is aimed at presenting specialized studies and research to the members of diversified society especially postgraduate students and ECD researchers.
The magazine is one of the publications that aim to communicate with a diversified audience, convey emergency and crisis culture and highlight NCEMA role and activities whether at the local or international levels. The audience can receive a hard copy of the magazine or download their copy from NCEMA official website or application. The copy will be advertised on the NCEMA accounts on social media.
Questionnaire Objective
Ensure that Emergency and Crisis magazine is delivered to audience.
Decision Making
NCEMA will seek to improve and develop the ways to communicate Emergency and Crisis magazine to the largest portion of diversified audience and implement the proposals presented.
Participate
Publications
The National Standard for Business Continuity Management System Download PDF
Responding to Weather Fluctuations and Bad Weather Download PDF
Emergency Evacuation and Sheltering Download PDF
Dealing with Tremors and Earthquakes Download PDF
National Emergency Crisis and Disaster Management Authority Download PDF
Occupational Health and Safety Management System Download PDF
………………………………………………………………………
Extreme heatHazard level: High ?
In the area you have selected (United Arab Emirates) extreme heat hazard is classified as high based on modeled heat information currently available to this tool. This means that prolonged exposure to extreme heat, resulting in heat stress, is expected to occur at least once in the next five years. Project planning decisions, project design, and construction methods must take into account the level of extreme hazard. The following is a list of recommendations that could be followed in different phases of the project to help reduce the risk to your project. Please note that these recommendations are generic and not project-specific.
According to the most recent assessment report of the Intergovernmental panel on Climate Change (IPCC, 2013), continued emissions of greenhouse gases will cause further warming, and it is virtually certain that there will be more frequent hot temperature extremes over most land areas during the next fifty years. Warming will not be regionally uniform. In the area you have selected, the temperature increase in the next fifty years will be slightly higher than the worldwide average. It would be prudent to design projects in this area to be robust to global warming in the long-term.
Recommendations
- VULNERABILITY ASSESSMENT: The high-level information available in ThinkHazard! indicates the presence of extreme heat hazard in your project area. Before committing significant resources to this issue, you should further evaluate if your project is vulnerable to extreme heat and whether a more detailed assessment and/or intervention should be considered. More information
- SEEK INFORMATION: Obtain pre-existing extreme heat hazard information. ThinkHazard! predominantly uses global datasets, therefore for more detailed project planning you should determine the availability of pre-existing local extreme heat hazard information to check whether your project is indeed located in regions prone to extreme heat. In this respect, it should be noted that large built-up areas such as cities or harbors are more likely to experience excess heat than rural areas, because of the urban heat island phenomenon. More information
- PROFESSIONAL GUIDANCE: Consultation with engineering and climate impact assessment professionals will provide a more detailed understanding of the risk posed to your asset by extreme heat. The level of guidance required will depend upon the level of hazard present, the vulnerability of the asset and local legislation that might apply. More information
- MONITORING AND FORECASTING: Identify extreme heat monitoring and forecasting systems. These are designed to provide communities with advanced warning of extreme heat based largely on information contained in weather forecasts, complemented with temperature monitoring. They can be used to trigger protocols (e.g., the deployment of heat-health action and emergency response plans) to mitigate against the effects of extreme heat. More information
- INTERDEPENDENCY: Consider vulnerability of other assets within the project’s dependency network: If your project is interdependent with other projects, it is important to assess the vulnerability of the entire network if the service provided is critical. More information
- HEAT MANAGEMENT: Your project or development should consider heat management measures appropriate to your sector of operation, for example, technological adaptation, building design, or changing working practices. More information
- AVOID INCREASING HAZARD: Built infrastructure may alter heat hazard. Constructing a significant piece of infrastructure can significantly alter the thermal properties of the area, generally inducing higher temperatures. Any newly built infrastructure covering large enough areas (e.g., new city quarter or harbor zone) should be undertaken with consideration as to how this will influence the local microclimate. More information
Most useful documents on Climate and Multi-hazard risk in the United Arab Emirates
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
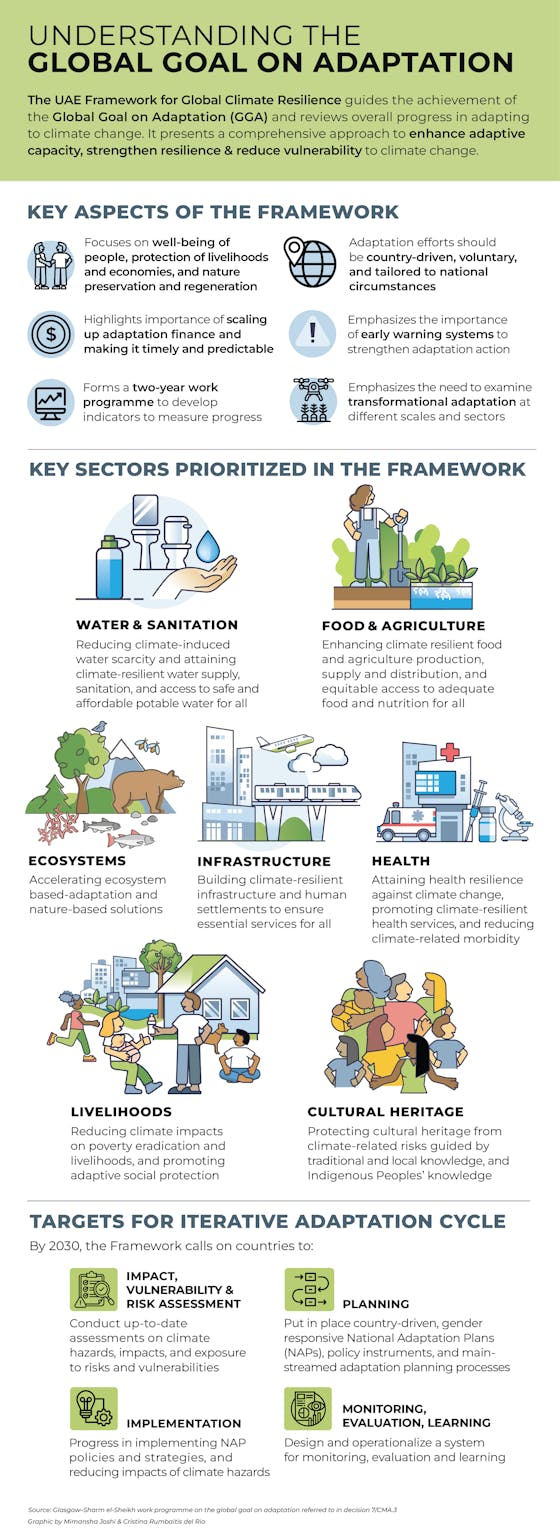
The UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience uniquely positions climate adaptation — the process of building resilience to global warming’s current and future impacts — as a top priority for all nations.
Adopted in December 2023 at the United Nations Climate Change Conference (COP 28) in Dubai, it is the first international declaration of its kind with climate adaptation as the primary focus.
What is the UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience?
The framework is the culmination of two years of workshops and consultations with hundreds of government officials, scientists, and advocates. It expands on the Global Goal on Adaptation (GGA), which was established in the Paris Agreement in 2015. The UAE Framework will improve our ability to measure progress on the GGA and maintain accountability. More broadly, the framework’s adoption signals the need for accelerating global action on, and support for, adaptation — which until now has not received the same level of funding or attention as other aspects of the Paris Agreement.
While the framework does not establish a headline target akin to the Paris Agreement’s global warming threshold of staying within 1.5° C above preindustrial temperatures, it does place focus squarely on the “collective well-being of all people, the protection of livelihoods and economies, and the preservation and regeneration of nature, for current and future generations, in the context of the temperature goal.” In other words, the well-being of people and the planet serves as the framework’s guiding star. It also prioritizes key sectors for increased climate resilience, including food and agriculture, water, cities and infrastructure, ecosystems and nature, health, livelihoods, and cultural heritage, sending an important message to practitioners in these sectors that urgent action on climate adaptation will be necessary for humanity to survive.
In addition, the framework details a series of targets linked to different stages of the country-level policy cycle required to achieve these adaptation goals. It lays out clear and concrete steps that start with government-led assessments of each nation’s unique climate risks and vulnerabilities, which will inform the creation of a national adaptation plan, followed by implementation and ongoing evaluation of progress in reducing climate vulnerability.
Next Steps for the UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience
- Measuring progress toward the Global Goal on Adaptation: The framework establishes a two-year UAE–Belém work program – so named for the host cities of COP28 and COP30 – to develop more specific and standardized indicators for measuring progress toward the targets it outlines. It will be essential for the new Dubai action plan to build upon already existing agendas like the Sustainable Development Goals, the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, and other multilateral agreements that have relevant indicators. This process will need to incorporate the expertise of scientists, researchers, and practitioners across the globe to ensure that we are measuring what matters and not just what is easiest to measure.
- Financing critical adaptation needs: While the UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience marks a crucial step forward, the international community must also find innovative and creative ways to mobilize financial resources, especially for developing economies, to realize the promise of the Global Goal on Adaptation. These investments must be both larger and more flexible than current financing if low-income nations are to meet the level of ambition on climate adaptation outlined in the new framework.
Featured resource
Adaptation Campaign Hub
Adapting to climate change is not a choice, it’s a vital priority. The Adaptation Campaign hub features key messages, dates, events, campaigns, and resources focused on advancing adaption globally.
Featured Events
November 10–21, 2025
30TH SESSION OF THE CONFERENCE OF THE PARTIES (COP 30)
COP 30 will be hosted in Belém, Pará, Brazil, where world leaders, scientists, non-governmental organizations, and civil society leaders will gather to discuss actions to tackle climate change issues such as adaptation, resilience, renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and more.
Learn more >>
Past Events
September 23, 2025
ADAPTATION IS LIFE: SCALING UP FINANCING FOR ADAPTATION ON THE ROAD TO COP 30
DanChurchAid, UN Foundation, and Talanoa hosted an event on the sidelines of the 80th Session of the UN General Assembly and New York Climate Week that examined the critical importance of adaptation to development, growth, stability, and equity, and profiled several new mechanisms being developed to bring adaptation and loss and damage finance to scale.
Learn more >>
October 1, 2024
Options for a Strong Adaptation Outcome in the New Collective Quantified Goal for Climate Finance
The UN Foundation and Germanwatch hosted a timely discussion on how the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG) can better reflect the urgent needs of adaptation finance as the world faces increasing climate impacts.
Learn more >>
SEPTEMBER 24, 2024
HIGH LEVEL ROUNDTABLE: SCALING UP ADAPTATION FINANCE AND ACTION AT COP-29
Hosted by DanChurch Aid, UN Foundation, E3G, and Germanwatch, this roundtable hosted high level speakers and representatives from the media, civil society, think tanks, and practitioner organizations from the Global North and Global South to discuss and agree on the future of climate finance under the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
Learn more >>
April 2, 2024
NAVIGATING THE YEAR OF CLIMATE FINANCE: THE NEW COLLECTIVE QUANTIFIED GOAL (NCQG) AND IMPLICATIONS FOR ADAPTATION FINANCE
The UN Foundation and Germanwatch hosted this session about the New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG) and what it means for climate adaptation finance. Experts will share their reflections on the state of play of the NCQG negotiations and expectations for the year ahead.
Learn more >>
February 7, 2024
Webinar on the UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience: Insights from COP 28 and Future Perspectives
The UN Foundation convened a webinar on the new UAE Framework for Global Climate Resilience. Experts shared their reflection on the adaptation outcomes of COP 28 and previewed what comes next for the framework in 2024. In this webinar, we delved into the global implications of the framework for adaptation action and discussed the necessary steps for it to fulfill its promise in the coming year.
Learn more >>
Technical Papers
Linkages Between the New Collective Quantified Goal and the Global Goal on Adaptation
Produced by C2ES and the United Nations Foundation, this paper evaluates the existing language promoting NCQG-GGA linkage and potential indicators for progress — and how the NCQG can facilitate a better prioritization of adaptation finance. (October 2024)
Read the Paper >>
Transformational Adaptation for COP29
Transformational adaptation is an evolving concept within climate adaptation and resilience literature, emphasizing systemic shifts that address root causes of vulnerability while considering the spatial scale of changes. Key features include durable interventions and the potential for broader systemic transformations, though definitions vary. The upcoming sixth meeting of the Parties to the Paris Agreement (CMA6) in November 2024 will be a crucial platform for clarifying this concept across sectors and scales, showcasing implementation examples, and discussing assessment methods for transformative strategies. This paper examines options for defining transformational adaptation within the UNFCCC context, building on outcomes from COP28 as Parties prepare for CMA6. (September 2024)
Read the Paper >>
NCQG: The Role of Different Sources For Adaptation Finance
This publication provides an overview of the relative roles that different sources of finance and different instruments can play in the scaling of adaptation finance, within a New Collective Quantified Goal (NCQG) that is structured on a combination of thematic subgoals and sources to ensure adequate provision of adaptation finance under the NCQG. (September 2024)
Read the Paper >>
Views on the UAE-Belém work programme
This submission, co-authored by 15 UN entities, provides recommendations regarding the modalities of the UAE–Belém work programme. (March 2024)
Read the paper >>
Options for a PolitIcally-Salient Headline for the Global Goal on Adaptation
The outcome of the Paris Agreement established the Global Goal on Adaptation, not as a quantitative goal but as a shared aspiration. Several different formulations for an overarching goal have been proposed formally and informally through the Glasgow Sharm el-Sheikh work program and related discussions. In this brief, co-authored by the UN Foundation’s Cristina Rumbaitis del Rio and Kaveh Guilanpour from C2ES, some of these proposals are explored while highlighting their benefits, drawbacks, and considerations. (November 2023)
Read the paper >>
Compilation of Illustrative Targets and Indicators for the Global Goal on Adaptation
One of the objectives of the Glasgow Sharm el-Sheikh work program is to enhance understanding of the Global Goal on Adaptation, including of the methodologies, indicators, data and metrics, needs and support needed for assessing progress towards it. This submission includes a compilation of indicative targets and indicators from selected existing international agreements that can be used to support this process. (May 2023)
Read the paper >>
Prioritizing Transormational Adaptation
This technical paper briefly identifies what we see as the most salient proposed adaptation metrics currently under consideration. It also argue for the importance of the transformative adaptation approach and identifies its five defining features and enabling factors. (March 2023)
Read the paper >>