Still under construction…………..
National Disaster Reduction Centre of China (NDRCC)

The National Disaster Reduction Center of the Ministry of Civil Affairs of the People’s Republic of China was established in April 2002 and joined the “Ministry of Civil Affairs Satellite Disaster Reduction Application Center” brand in February 2009.The center mainly undertakes the data and information management of disaster reduction and relief,disaster and risk assessment,product and service, space science and technology application,science and technology and policy research,technology equipment and supplies research,publicity and education,training and international exchange and cooperation and other functions,proving information service,technical support and decision-making advice for the government’s disaster reduction and relief work.
NDRCC is the National Disaster Reduction Centre of China. NDRCC is an agency providing information and technological support, including a national disaster database which local civil affairs departments access to enter details about the disaster.
NDRCC is a very strong supporter of the UN-SPIDER progamme and is hosting the UN-SPIDER Beijing Office.
National Disaster Reduction Center

The State Flood Control and Drought Relief Headquarters launched a level 4 emergency response for flood and typhoon prevention in Guangdong and Hainan
Send a working group to Guangdong to assist and guide
A tropical depression formed over the central and eastern South China Sea on the evening of the 5th . It is expected to intensify into the 16th typhoon of the year on the 6th , then move toward the central and western coasts of Guangdong, making landfall there between the night of the 7th and the morning of the 8th (at severe tropical storm or typhoon levels). As a result, heavy rain and strong winds will occur in southern China and the South China Sea from the 6th to the 10th , with heavy to torrential rain expected in central and southern Guangdong, with some areas experiencing heavy rainstorms and locally extremely heavy rainstorms ( 250-350 mm).
In accordance with the “National Flood and Drought Relief Emergency Plan” and relevant regulations, the State Flood Control and Drought Relief Headquarters decided to launch a level-four emergency response for flood and typhoon prevention in Guangdong and Hainan at 18:00 on September 6 , and sent a working group to Guangdong to assist and guide flood and typhoon prevention work.
National Disaster Reduction Center News
https://www.ndrcc.org.cn/jzzxyw/index.jhtml.

Disaster Prevention and Mitigation
Updated: 21-02-2025 ,Source: CMA
For many years, CMA has made every effort in terms of disaster prevention work. For different stages of meteorological disasters, CMA provides phased forecasting and early warning service products accordingly, and fully mobilizes departmental emergency coordination and social forces in this process, so that meteorological monitoring, forecasting and early warning information can be quickly transformed into disaster prevention and mitigation action for governments at all levels and the public. This progressive meteorological service mechanism has been elucidated by unique explorations in various regions.

At 16:00 on July 23, 2023, the “1262” progressive service mechanism was launched by Fujian Provincial Meteorological Service in response to the first typhoon that made landfall in Fujian this year, Typhoon “Doksuri”. With the coordinated efforts by the Service and the local government, key prevention areas were designated in advance and the district-based and sector-based hierarchical command system was established for rescue force deployment and personnel evacuation. In this case, FMS provided accurate weather forecast for the countermeasures of different sectors.
In the flood season of 2022, Shangluo, Shaanxi Province, was hit by multiple rounds of heavy rain, which damaged farmland dykes, cut off roads and destroyed infrastructure facilities. The “dual 2 mechanisms plus 5 measures” disaster prevention and mitigation mechanism of Shangluo, guided by meteorological forecasting and early warning, was employed to fight the rainstorm.
From 14:00 to 20:00 on June 30, 2020, Daliankou Village of Xiakou Town, Jiangshan City, which is the subordinate administrative area of Quzhou, Zhejiang Province, encountered heavy rainfall, causing multiple disasters such as flash flood, landslide and debris flow. Jiangshan City utilized the “grid+meteorology” mechanism to successfully transfer a total of 198 Daliankou villagers from 94 households in dangerous areas, and saved 11 trapped villagers.
From 07:00 on July 9 to 07:00 on July 10, 2024, heavy rain occurred in Dazu District in Chongqing, with the maximum rainfall registering 169.2 mm. After receiving the early warning information from the meteorological office, Longshui Town transferred 323 people at stake in advance, of which 4 were urgently transferred and relocated.
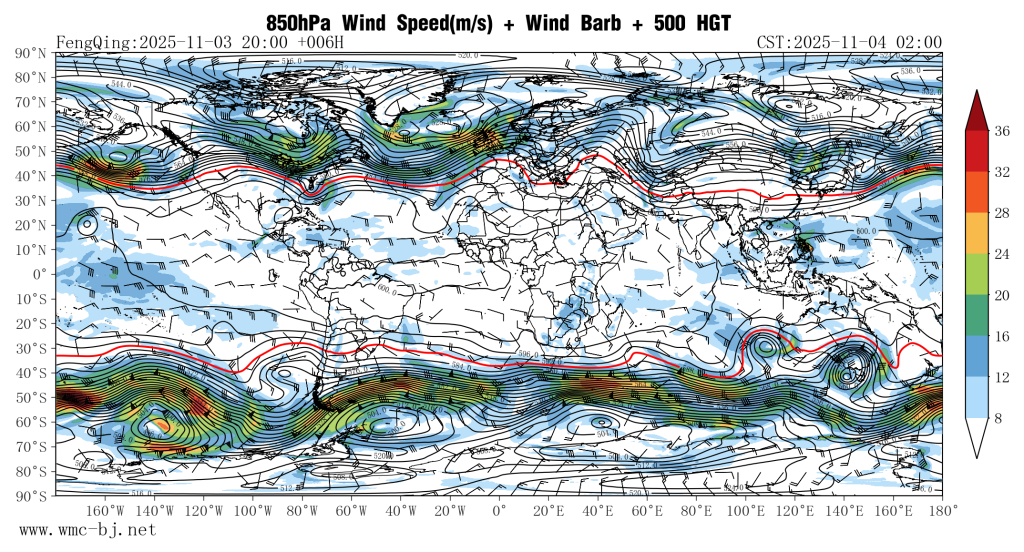
Numerical Weather Prediction
Updated: 17-11-2023
Source: CMA
NWP
Through continuous research and development of core technologies, China Meteorological Administration (CMA) has steadily improved the performance of its numerical weather prediction (NWP) models, and has completed the research and development of the CMA Global Assimilation Forecasting System (CMA-GFS) with a resolution of 12.5 kilometers, the CMA Regional Numerical Forecasting Model with a resolution of 1 kilometer and a one-hour update (CMA-MESO), and has established an ensemble forecasting system with a resolution of 50 kilometers for the whole world, and a resolution of 10 kilometers for the Chinese region. It has established a global ensemble forecast system with 50 km resolution and a Chinese regional ensemble forecast system with 10 km resolution, a first-generation global atmospheric reanalysis system with 34 km resolution, and specialized NWP systems for sand, dust, haze and typhoon, and has developed a scientific and technological innovation platform for coordinating the research and development of NWP.
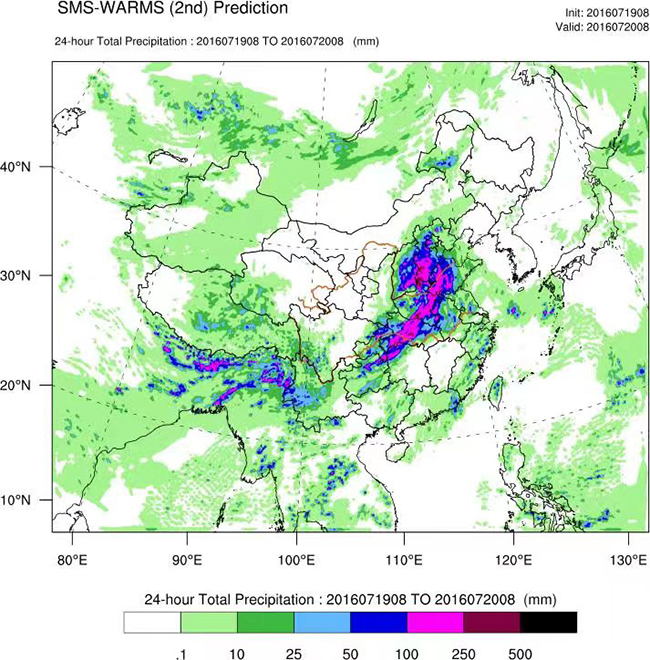
At present, it has developed the domestically produced Advanced Radiative Transfer Modeling System (ARMS), with a ratio of more than 80% for the assimilation of satellite data into NWP models, of which the proportion of FENGYUN satellite is increased to 14%, and the available forecast days are 8.0 days in the Northern Hemisphere and 8.5 days in East Asia. Heavy precipitation forecast better solves the problem of refined forecasting and early warning service of catastrophic weather, and becomes an important scientific and technological support for CMA’s strong weather forecasting business for meteorological stations at all levels.It is capable of detecting and forecasting tropical cyclones in global waters, and plays an important role in global navigation operations, monitoring and forecasting of marine meteorological disasters in the north-west Pacific Ocean and the northern Indian Ocean, as well as the “Belt and Road” meteorological service.In addition, the continuous upgrading of NWP systems for sandstorms, fog-haze and ocean waves has significantly enhanced China’s meteorological support capabilities in areas such as disastrous weather response and serving local economic and social development.At the same time, it has successfully provided meteorological support for some major events like Beijing 2022 Olympic and Paralympic Winter Games.
Grid Forecasting
Updated: 17-11-2023
Source: CMA
Currently, the Central Meteorological Observatory has established a seamless intelligent digital grid forecasting technology and product system.
Based on multi-source and multi-scale numerical model forecasts, supplemented by enhanced observations across the country and the fused real-time analysis field of China, the Central Meteorological Observatory utilizes new post-processing techniques such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to construct a comprehensive product system. This system includes minute-level rolling nowcasting, hourly updated short-term forecasts, scheduled short-to-medium term forecasts, and daily extended-range forecasts at a national resolution of 5 kilometers and a time scale of 0-30 days with intervals of 10 minutes/1 hour/3 hours/12 hours. Globally, forecasts are provided at a resolution of 10 kilometers and a time scale of 0-10 days with intervals of 1 hour/3 hours. The seamless intelligent digital grid forecasting product system has been made available to more than 10,000 cities worldwide, offering accurate point-to-point forecasting services. Validated results show that the grid forecast accuracy is significantly better than mainstream raw model forecasts at home and abroad, making it advantageous compared to similar international forecast products.
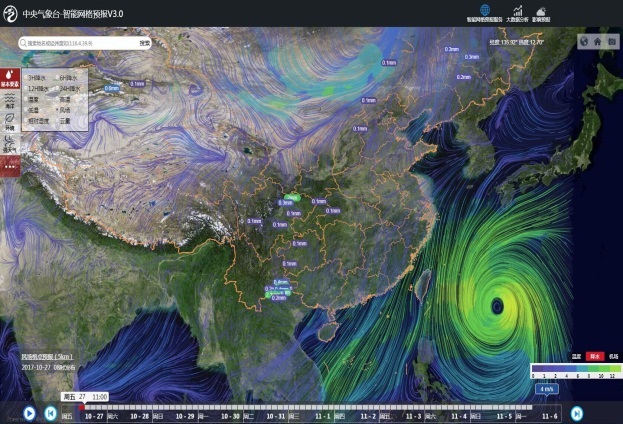
Meanwhile, the Central Meteorological Observatory has developeda refined forecasting technique for importantlocationsduring major events. This technique uses machine learning and fusion to create an objective and high-resolution forecast for single points, called STNF (Single-point Targeting and Fine-grained) forecasting. It can predict temperature, wind, and precipitation at one-hour intervals for 72 hours at specific locations, even under complex terrain conditions. This advanced forecasting capability has provided strong support for the fine-grained forecasting requirements of major events, such as the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics. During the event, the STNF objective and high-resolution forecasts outperformed similar products in various element products’ scores, including first-ranked short-term forecasts of gusts and wind direction. The accuracy of these forecasts was over 10% higher than similar forecasting products.
Climate model
Climate models have been developing in CMA since 1995. The first-generation climate model was developed from 1995 to 2004, namely Beijing Climate Center ocean-atmosphere Coupled Model BCC-CM1.0. This model was used for seasonal climate prediction in China. During 2005-2011, a new fully-coupled climate (BCC-CSM) was developed. Two versions of the BCC-CSM model were released in 2012, namely, BCC-CSM1.1 with a coarse horizontal resolution T42 (~280km) and BCC-CSM1.1m with a medium horizontal resolution T106 (~110km). Both versions performed CMIP5 experiments. The released data have been widely used. The models are further developed with three versions during 2012-2020, including a median-resolution model BCC-CSM2-MR (~110km), a high-resolution model BCC-CSM2-HR (~45km) . These models all participated in CMIP6 and released the simulation data in 2018-2019. Climate models BCC-CSM1.1m and BCC-CSM2-HR are also used in S2S and climate prediction in China. CMA has been developing the third-generation models since 2016, including BCC-CSM3 (~30km) , which will participate in CMIP7.
Climate Projection
Updated: 17-11-2023
Source: CMA
China Meteorological Administration (CMA) provides climate forecasting services that focus on predicting and preparing for potential disasters. Diverse diagnostic and analytical products have been created to address various high-impact climate disasters, including high temperatures, heavy rainfall, low temperatures, and typhoons. Deterministic and probabilistic objective forecasting products at the sub-seasonal timescale have been developed based on dynamic climate models. A climate disaster diagnostic and forecasting platform has been established and widely applied in national and provincial 10-30-day lead-time and monthly forecasting operations.
CMA has fully developed climate event forecasting services. Operational capacity building has been conducted for significant climate events during the East Asian summer monsoon, including monitoring and forecasting key circulation patterns and the onset and development processes of winter/summer monsoons. Monitoring and forecasting products have been established for the pre-flood season in South China, the plum rain, the rainy season in North China, and the autumn rain in Western China,so as to establish a comprehensive operation for the monitoring, diagnosis and forecasting of the rainy season process. Sub-seasonal to seasonal forecasting products have been developed for the key atmospheric circulation systems influencing the early or late onset of various rainy seasons, establishing objective forecasting services for climate events at the sub-seasonal to seasonal timescale.
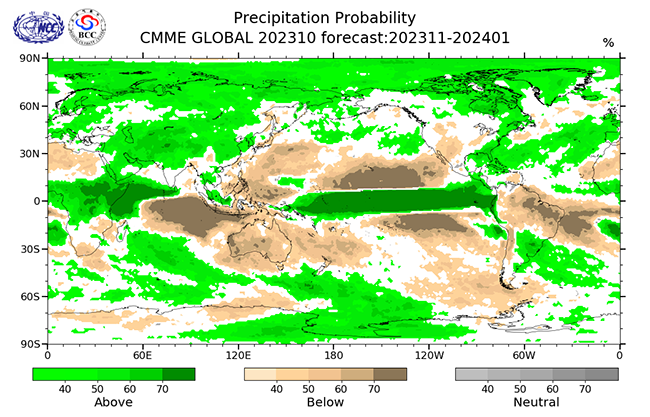
Global climate forecasting services have been enhanced to provide real-time monitoring of basic meteorological factors and deterministic and probabilistic forecasting services at multiple time scales. These services now include 10-30 day, monthly, and seasonal forecasts. Monthly and seasonal climate forecasting services are available for various factors such as global atmospheric circulation and monsoons, important atmospheric circulation patterns in the Northern Hemisphere, global sea surface temperatures, El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), global snow cover, and global sea ice.
Monthly Global Climate Monitoring and Forecasting Reports are published and an Annual Global Climate Status Report is released each year to provide a comprehensive view of the planet’s climate condition.
Information System
Updated: 17-11-2023
Source: CMA
CMADaas
CMADaas, the cloud-based meteorological big data platform, is a “processing plant” for China’s massive meteorological data, which comprehensively manages and provides meteorological “data, computing power and algorithm” resources, and supports “cloud + terminal” meteorological operations. And it is the basic pillar for the construction of the “cloud + terminal” operation technology system and the high-quality development of meteorological enterprises.
On 15 December 2021, CMADaas was officially put into operation. Its feature of “digital and algorithmic integration” can integrate data and algorithmic resources of the meteorological industry, make the algorithm close to the data, and realize a high degree of integration of data management, processing and application services, as well as effective connection and organic interaction between various businesses and systems, thus solving the redundancy problems brought by repeated calls, storage and transmission of data by various business systems in the past, and contributing to the establishment of a modern meteorological business technology with breakthroughs in technology, a more integrated and intensive layout, more efficient and smoother processes, and more open and integrated mechanisms. This will solve the problem of redundancy brought about by repeated calls, storage and transmission of data by various operational systems in the past, and lay a solid foundation for the construction of a modern meteorological operational technology system with breakthroughs and improvements in technology, a more integrated and intensive layout, a more efficient and smooth process, and a more open and integrated mechanism. At present, the operational systems of meteorological services at all levels across the country are accelerating their integration into the cloud-based meteorological big data platform, and various types of systems are expected to strengthen their integration, further bridging the gap between scientific research and operations, between the State and the localities, and between the various links of the operational chain, so as to promote the information system towards a higher degree of integration and intensification.
Tianjing system
The meteorological integrated real-time monitoring system -“Tianjing”, realizes the intensive national meteorological integrated monitoring and operation and maintenance, which adopts vivid forms of expression to visually present the national meteorological information resource capacity and operation status, and system operation status, etc., and the whole process of data flow, so as to explicitly display the national meteorological informatization operation.

“Tianjing” system realizes an integrated horizontal and vertical monitoring layout. Through intensive transformation, on-duty personnel can monitor and deal with problems of different systems in a unified manner through “Tianjing”, and tasks of different priority and difficulty are distributed to technicians through various channels to ensure that faults are dealt with in a timely manner. The station-provincial-national coordinated monitoring, operation and maintenance system can make the results of the system benefit the operation and maintenance of meteorological services in the country. The set-up of the “Tianjing” system ushers in a new era of integrated monitoring, operational control and operation and maintenance services for meteorological services.
Tianheng Tianyan
“Tianheng Tianyan” is a comprehensive meteorological observation product system integrates weather radars, wind profiles, cloud radars, microwave radiometers, large-scale unmanned aerial vehicles, and data related to lightning, water vapor, ground, sounding, ecology, atmospheric composition, oceans and other multi-source data information, which is characterized with diversified observations, and massive and informative data. By means of artificial intelligence identification, big data fusion analysis and other techniques, for the real-time or real-time accurate monitoring and early warning of hails, thunderstorms and gales, tornados, heavy precipitation, typhoons etc., it develops radar quantitative estimation of precipitation, multi-band radar mosaic, severe convection identification with high-resolution, hail tracking and positioning, 3-D grid wind field, 3-D typhoon warm-core, upper- and low-level attitude rapids, rain and snow phase identification, and minutes-resolution multi-element vertical profile; as well as the global observation requirements, it conducts research on several customized global products such as SST fusion products and assessment of the global network of stations. There are 628 kinds of observation products in “Tianheng Tianyan”.
With the starting point of the strengths of advanced precise observation technologies and the aim to promote high-quality, refined monitoring application and services, “Tianheng Tianyan” has realized full range of smart and targeted services with observations ranging from “CT” to “holographic” level, from China to globe, from direct to remote sensing, and from real-time to full coverage of historical process.
Early warning
Updated: 21-02-2025, Source: CMA
China has gradually formed an early warning model of “government-led, warning-triggered, cross-department coordination, and public participation”. The Chinese government has formulated a series of laws, regulations, standards, systems, and emergency plans for disaster prevention and mitigation. Through early warning information, governments and relevant departments at all levels are able to carry out meteorological disaster prevention and mitigation measures in an orderly manner. Meanwhile, every effort has been made to promote the national comprehensive risk survey of natural disasters so as to provide authoritative information and scientific decision-making basis for effective implementation of natural disaster prevention and control.

When dealing with major disastrous synoptic processes, CMA assesses the risk of meteorological disasters in advance and, as the synoptic process approaches, keeps updating forecasting and warning services of higher spatiotemporal resolution and accuracy. At the same time, a meteorological disaster risk prediction model has been established based on disaster types, industries, regions, and time periods. Relying on the national emergency warning information release system, the national-, provincial-, city- and county-level early warning hierarchy has been established and 16 different sectors and industries have been connected within the system. 82 types of early warning information can be gathered, shared and sent out in a “one-button” mode. In addition, through customized services and localized deployment, early warning information can be spread out extensively.
China has also created a high-level “call for action” mechanism for early warning, which means that when major disastrous weather is about to or has already occurred and is highly likely to cause a major disaster, CMA will provide “point to point” reminders to government leaders and heads of disaster related departments in advance. Under the emergency coordination mechanism led by meteorological early warning, a refined and detailed classification of early warning response grades has been provided and China has gradually established a mechanism for suspending classes, production activities, operation, and business in high-risk areas and highly sensitive industries under extreme weather conditions. At the same time, a total of nearly 400000 meteorological information personnel have received training and are expected to enter schools, rural areas, enterprises, and communities for the enhanced disaster prevention and mitigation capabilities of the whole society.
In 2024, during COP29, Early Warning for Climate Change Adaptation:China’s Action was unveiled.
Agricultural Service
Updated: 21-02-2025, Source: CMA
Specialized meteorological services have been provided for key agricultural seasons, for monitoring, forecasting and early warning of agrometeorological disasters, and for agricultural disease and pest prevention and control. Photovoltaic-integrated meteorological service has been strengthened. Other agriculture services include the following: “Chinese natural oxygen bars” and “climate friendly products” in rural areas, 1282 public welfare posts for meteorological observation and weather modification, targeted assistance to Tuquan, Inner Mongolia and assistance by agricultural products consumption.

At the same time, CMA is making efforts to promote the pilot projects for the supply side reform of agrometeorological service and the pilot projects for seed industry meteorological service. The national exert team for agrometeorological service has been established to optimize the agrometeorological service system. And in order to enhance the meteorological disaster prevention and mitigation capabilities in rural areas, the standardization construction of the “Six Ones” for grassroots meteorological disaster prevention and mitigation has been completed, with the full coverage of town-level automatic meteorological stations.
CMA has also collaborated with the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs to promote the quality and efficiency of agrometeorological service. 15 characteristic agrometeorological service centers have been built to drive the meteorological services of various provinces (autonomous regions, municipalities) to establish provincial-level characteristic agrometeorological service centers. And regular consultations have been held to strengthen agrometeorological disaster risk warning. Tailor-made services have been provided to agricultural machinery operators and related personnel.
Weather Modification
Updated: 21-02-2025, Source: CMA
In recent years, China’s weather modification efforts have developed rapidly, and its operational capacity and management level have been continuously improved, which have played an important role in serving agricultural production, supporting disaster prevention, mitigation and relief, supporting ecological civilization and safeguarding major emergency events.
In the area of ensuring food security, great efforts have been made to vigorously implement artificial rain (snow) enhancement and hail suppression measures, with the current average annual rain augmentation area stabilizing at 5 million square kilometers and the average annual hail suppression area at around 650,000 square kilometers, contributing to bumper grain harvests in successive years.

To ensure ecological safety, large-scale and regular artificial rain (snow) enhancement operations have been continuously carried out to replenish ecological water in a timely manner and provide meteorological support for soil and water conservation, vegetation restoration and biodiversity protection. Ecological restoration-type weather modification operations have been piloted throughout the Qilian Mountains, the Sanjiangyuan Region, the Tianshan Mountains, the Danjiangkou and other typical areas.
To ensure water security, we have actively carried out artificial rain (snow) enhancement to respond to drought conditions, in an effort to help reservoirs replenish water and increase capacity in arid areas, and protect drinking water for people and livestock, industrial and agricultural production.
In terms of supporting major emergency events, we have worked on weather modification for disaster prevention, mitigation and relief and emergency response with great success in disaster prevention, such as fighting forest fires and reducing the risk of forest fires.
Industry Service
Updated: 21-02-2025, Source: CMA
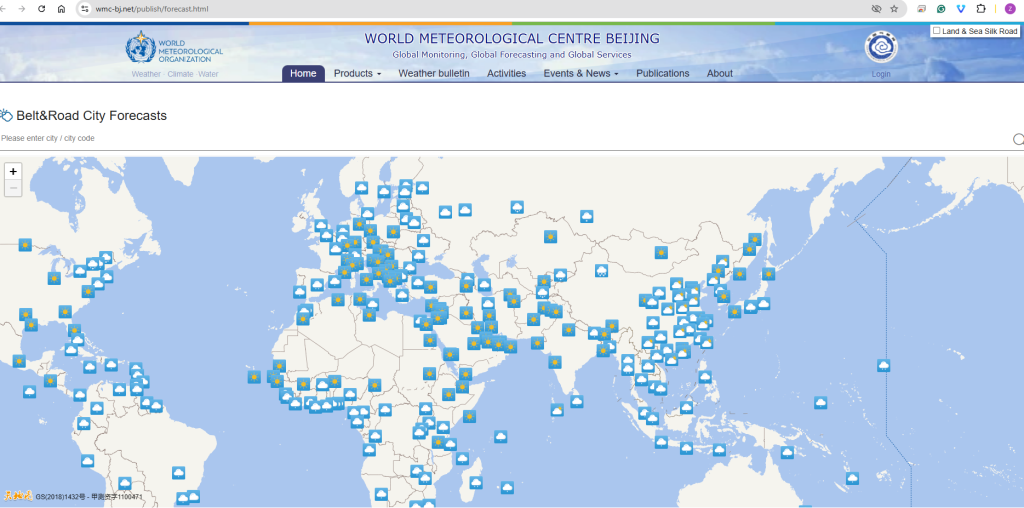
City Forecasts

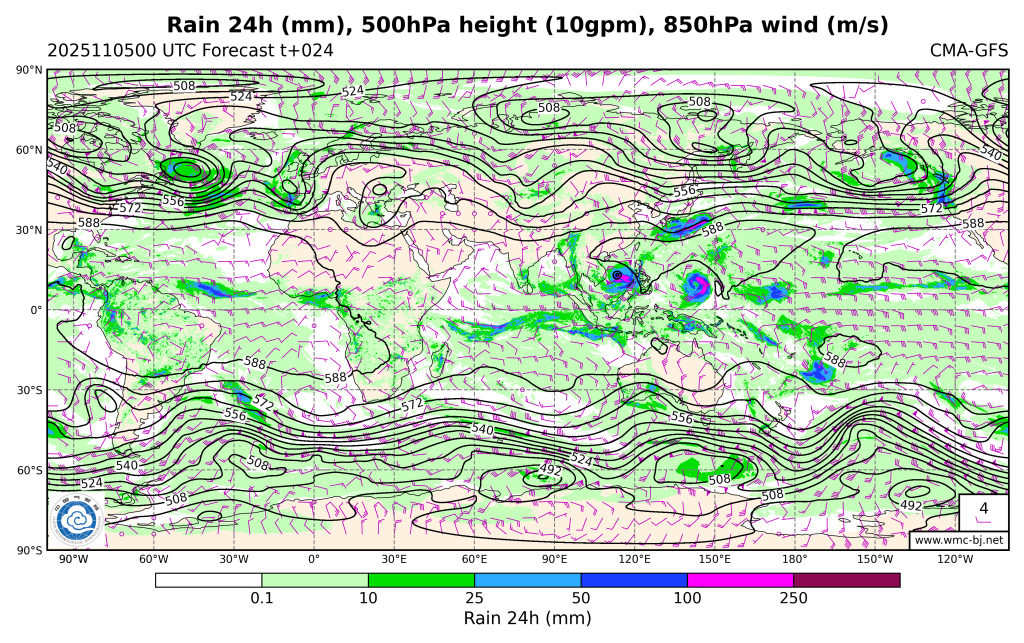
Surface Convective Precipitation

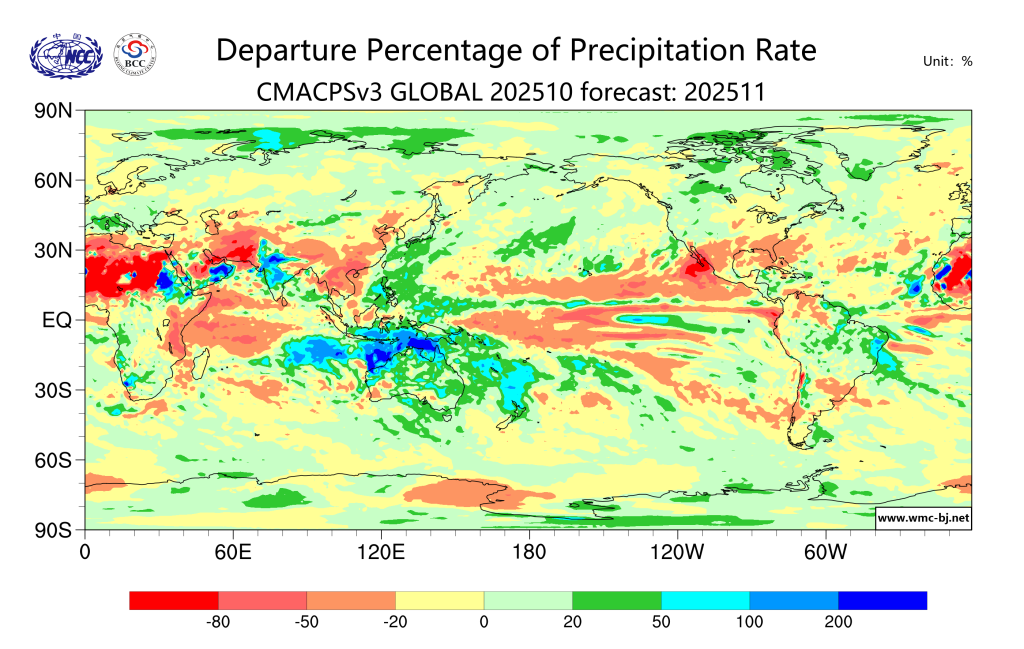
Sattelite Image

Transportation Meteorological Service
China Meteorological Administration (CMA) has responded to national demands by providing meteorological support for robust transportation development. In conjunction with the Ministry of Public Security, the Ministry of Transport, the State Railway Administration, and the State Postal Bureau, CMA has released the “14th Five-Year Plan” on Meteorological Support for Transportation. The goal is to explore the development of a contemporary, comprehensive transportation meteorological service platform. CMA offers tailor-made transportation meteorological service in terms of disasters, road sections, waterways, seas, and railway routes.

Based on the three-dimensional space, ground, air and sea-based transportation meteorological monitoring network, a modern transport meteorological service system integrating real-time monitoring, accurate forecasting, disaster warning and risk assessment has been established using physical mechanisms, machine learning, coupled interpretation and other technical means. CMA provides digital and refined meteorological factors forecasting products for transportation of any location in the country, with a time scale ranging from 10 minutes (short range and nowcasting) to monthly and seasonal scales. At the same time, with the fusion of multi-source traffic information, CMA provides traffic weather risk prediction and warning services for the impact of severe weather in different scenarios, such as engineering design, facility maintenance, operations and maintenance, safety management, to meet the needs of risk research and collaborative decision making in the transportation field.
Inquiry services are provided to the public via the Internet, mobile clients and other means to protect drivers and passengers during their journeys. Customised traffic meteorological service information is integrated into the Traffic Safety Emergency Command System to meet the demand for emergency response to emergencies, holidays and major events, as well as severe weather prevention and mitigation. In recent years, CMA has endeavored to improve services for high-impact road sections, to expand transportation meteorological services for major construction projects, and to improve meteorological support for maritime transportation in ports and shipping lanes, as well as meteorological services for multimodal transportation with logistics.
Energy meteorological service
CMA conducts research and development of new energy meteorological services and products, including wind and solar energy resource assessment and forecasting, and energy and power meteorological disaster assessment. CMA’s operational resource assessment products mainly include a refined wind resource numerical simulation system, mesoscale wind resource numerical simulation products, a multi-source satellite remote sensing offshore wind resource monitoring and assessment system, a refined solar resource numerical simulation system, a satellite remote sensing solar resource monitoring system, and products such as a wind and solar resource complementarity index. Resource forecasting products include a wind-solar numerical prediction system (for the next 14 days) and monthly and seasonal wind-solar resource forecasting products. Energy and Power Weather Assessment and Forecasting products mainly include products such as forecasts of meteorological conditions for high temperature power loads in summer and forecasts of meteorological conditions for power line icing during winter cold spells.

CMA provides comprehensive and high-quality meteorological services to major new energy bases, government energy departments and energy enterprises. In terms of decision-making services, we have served 75 users, including the Operation Bureau of the Development and Reform Commission, the National Energy Administration and its dispatching agencies, provincial energy bureaus, member enterprises of the Electricity Safety Committee, the Atmosphere Department of the Ministry of Environmental Protection, and the North China Electricity Regulatory Centre. In terms of industry services, CMA regularly publishes the annual assessment bulletin of wind and solar energy resources for the industry and the forecast of meteorological conditions for wind and solar power generation in China. In terms of corporate services, CMA provides resource assessment services for pre-planning and siting of new power plants, and meteorological forecasting services for regional power grid planning, safe operation and power trading. These services have played an important role in supporting China’s new energy scientific planning and design, grid connection and consumption, and energy security. Under the guidance of the National Technical Committee for Standardization of Wind and Solar Energy and Climate Resources (TC540/SC2), CMA has taken the lead in formulating and revising more than 50 national/industry standards covering a wide range of areas such as wind and solar energy observation, forecasting and evaluation.
Ecological Meteorological Service
Through the scientific evaluation of characteristic climatic resources, the standardised creation of climatic and ecological brands, the comprehensive evaluation of the benefits of brand creation, and the promotion of demonstration and leadership, CMA has helped localities make use of advantageous climatic resources according to local conditions, and promote regional ecological value realization and green development, thus serving the local ecological civilization construction. “China Natural Oxygen Bar” is one of the first batch of China’s climate ecological brands, which is a useful practice of meteorological services to promote the transformation and development of local economy. In 2018, it was included in the “Guiding Opinions of the General Office of the State Council on Promoting the Development of Regional Tourism”; in 2020, it was listed in the “National Catalogue of Retained Projects for the Creation of Demonstration Activities” of the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Welfare (the second batch); and in 2022, it was included in the “Guidelines on Promoting the High-Quality Development of Meteorology (2022-2035)” issued by the State Council.

By the end of 2022, 313 sites in 29 provinces (autonomous regions and municipalities) were awarded the title of “China’s Natural Oxygen Bar”. In 2022, “China’s Natural Oxygen Bar Evaluation Bulletin” was published for the first time to the public, and “China’s Natural Oxygen Bar Green Paper” was published four times for the industry. A demonstration platform for the establishment of climate and ecological brands of CMA was built to support the establishment and demonstration of three climate and ecological brands such as “China Natural oxygen Bar”.
CMA strives to promote the climatic quality of special agricultural products. From 2019, the meteorological services of China will make full use of their scientific and technological advantages, focusing on local special agricultural products, and conduct research on the evaluation methodology of “Good Climate Products” and the practice of technical services. Relying on the independently researched and developed “Climate Quality Evaluation and Application Technology for Agricultural Products and based on Multi-source Data Integration” and the automated support platform, it will carry out regional kilometer-level climate quality evaluation, quality traceability, branding support and other technical services, effectively contribute to improving the climatic value-added of agricultural products and market competitiveness, and provide technical support for building regional community brands of special agricultural products and industrialized development.
Hydro-meteorological Service
The National Hydrological Forecasting Centre of the National Meteorological Centre (NMC) provides crucial hydro-meteorological services at a national level. These services originated from the hydro-meteorological servicesin response to the devastating floods that occurred in 1998 in the Yangtze River, Nen River, and Songhua River basins. The services were officially launched in 2002 with the surface rainfall estimation and forecasting of the seven major river basins. Starting from 2003, based on the relevant agreements jointly signed by the Ministry of Land and Resources and China Meteorological Administration (CMA), the service of geological disaster meteorological forecasting and warning during the flood season was officially launched. In 2006, NMC issued formally the flood and waterlogging disaster meteorological risk warning to better provide meteorological services for preventing and controlling farmland and urban waterlogging. In 2015, the Ministry of Water Resources and CMA jointly released the flash flood disaster meteorological warning. In2016, the flood risk warning product for small and medium-sized rivers was officially introduced.

The hydro-meteorological forecasting and warning service for river basins aims to provide risk-based meteorological warnings for disasters such as floods, flash floods, and geological hazards caused by precipitation, based on impact forecast and risk warning concepts. The service has established a national-river-provincial-city-county level meteorological disaster risk warning service system, which effectively supports hydro-meteorological services for the seven major river basins, small and medium-sizedriver basins, and the national disaster prevention and reduction system.
At present, the hydro-meteorological forecasting techniques of NMC rely mainly on independently developed statistical-based threshold models for disaster risk assessment and distributed hydrological models. These techniques are built on a seamless intelligent grid forecasting system that utilizes big data analysis and artificial intelligence technologies to create a meteorology-hydrology-geology coupled forecasting model. Starting in 2019, NMC established a comprehensive analysis and consultation support platform to meet operational requirements better. This platform is continuously upgraded and improved to serve better the integrated and intelligent hydro-meteorological forecasting and warning services for river basins.
Urban Meteorological Service
In 2021, CMA optimized the layout of urban meteorological service from a holistic perspective by convening meetings, formulating and issuing a task list for addressing the problems, and strengthening guidance and support, all for the high-quality development of meteorological service in large cities. Over the years, the guarantee mechanism for high-quality meteorological development in large cities has been further improved. Large cities have strengthened core technical breakthroughs such as urban meteorological monitoring, impact-based forecasting, and risk warning. The construction of scientific and technological innovation teams in key areas of urban meteorology has also been strengthened for the enhanced supporting capabilities for urban meteorological operations. Efforts have been made to improve the capabilities for high-precision monitoring in urban areas and then to increase the accuracy of urban meteorological forecasting and the precision of urban meteorological services. The basic supporting capabilities of urban meteorological information has also been enhanced continuously.

Large cities need to strengthen cross-department cooperation, improve the coordination mechanism for meteorological disaster prevention and mitigation, and integrate into the construction of smart cities, digital cities, sponge cities, resilient cities, and safe development demonstration cities. They are expected to provide tailor-made meteorological services for the public and improve the applicability, convenience, satisfaction, and social benefits of public meteorological services. Meanwhile, the institutional advantages shall be fully leveraged to strengthen the efforts in project approval, fund investment, and policy support. Laws and regulations for urban disaster prevention and mitigation are to be optimized and the standard formulation and modification are to be reinforced. Hence, the capabilities of meteorological services for safeguarding the urban development will be greatly enhanced.



Spaced-based
Updated: 20-11-2023
Source: CMA
China’s efforts to develop Fengyun meteorological satellites have made major strides over the past 50 years, with the polar and geostationary meteorological satellite series achieving continuously stable operation to persistently provide data and product services globally. By the end of 2023, 21 Chinese self-developed Fengyun meteorological satellites have been launched successfully. Nine of them are in operation at present, the data and products are widely applied to weather analysis, numerical weather forecasting and climate prediction, as well as environment and disaster monitoring.
At present, FY-3 LEO (Low Earth observation) meteorological satellites have realized early-morning, morning, afternoon, drifting four kinds of orbital observations to obtain global data eight times a day. The operational LEO satellites in orbit contain FY-3C since 2013, FY-3D since 2017 and FY-3E since 2021. FY-3G and FY-3F were launched in 2023.

FY-2 and FY-4 geostationary meteorological satellites are positioned over the Equator and can carry out continuous minute-scale high frequency observation of the fixed area covering one third of the Earth. The operational GEO (Geostationary) satellites in orbit contain FY-2G, FY-2H, FY-4A and FY-4B.
Among them, FY-4B and FY-3E have completed the on-orbit commission testing, and were operational service in June 2022. FY-3G and FY-3F are entering the in-orbit testing after their successful launch in 2023.
Fengyun meteorological satellites play important roles in the global space programs of World Meteorological Organization (WMO). National Satellite Meteorological Centre(NSMC) keeps close cooperation with WMO, CGMS, CEOS, GEO, APSCO and other international organizations and EUMETSAT, NOAA and other satellite providers on instrument development, remote sensing application, data exchange and applications related to weather monitoring and forecasting.
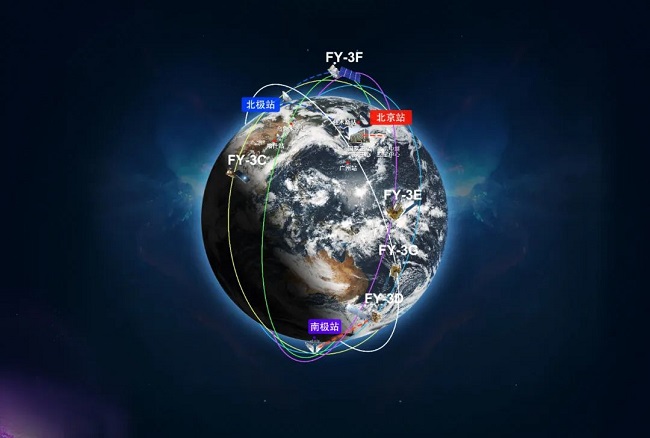
Meanwhile, CMA is deepening bilateral cooperation with international organizations and“Belt and Road”countries on Fengyun meteorological satellite application. Several online workshops were held to enhance remote sensing capabilities and data exchange. EUMETSAT and NSMC have built a long-term mechanism on remote sensing technologies. On 16 November 2021, A Global Space Weather Center was inaugurated. It is the first global center in China’s civil aviation meteorology field that is approved by International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). This center is the fourth global space weather center.
Since CMA introduced the Emergency Support Mechanism of Fengyun satellite (FY_ESM) in 2018, there are 32 countries registered for this mechanism by the Aug. 2023. FY-3D, FY-4A and FY-2H have officially become on-duty satellites of International Charter“Space and Major Disasters”. They have already provided relevant data service and monitoring service products for countries and territories like Madagascar, Mozambique and Malawi. In recent years, as on-duty satellites of CHARTER, Fengyun satellites have played increasingly significant roles in global meteorological disaster readiness, and served“Belt and Road”construction.

Ground-based
Updated: 22-11-2023
Source: CMA
By the end of 2022, a nationwide ground-based observation network consisting of 10,963 observation stations was established, including national climate observatories, atmospheric background stations, national climate reference stations, national basic stations, manned national (conventional) meteorological observation stations, national surface meteorological observation stations, national greenhouse meteorological observation stations, space weather observation stations, national agrometeorological observation stations, national agrometeorological experimental stations, national atmospheric constituent observation stations, and provincial meteorological observation stations.

At present, ground-based meteorological observation stations have achieved full coverage of towns and villages nationwide, with all stations fully automated, and the transmission efficiency of observation data has been increased from minutes to seconds. Initially, full coverage of the observation of key elements of basic climate variables in 65 climate zones nationwide has been made possible. The observation capacity of the specialized meteorological observation network basically meets the needs of major national strategies and economic and social development.

Air-based
Updated: 22-11-2023
Source: CMA
By the end of 2022, China had a total of 120 upper-air meteorological observation stations, as well as more than 100 wind profile radars and more than 900 GNSS/MET observation instruments. At present, China has built the world’s largest and most influential weather radar monitoring network, with basically localized radar hardware and software facilities. The reform of radar weather operation has been pushed forward, and the Radar Meteorological Centre has been established and brought into operation. China’s first S-band dual-polarization phased-array weather radar has been successfully developed and put into test operation. The new generation of weather radars fully realized “instant scanning and transmission”.

CMA continued to optimize the new generation weather radar operating software (ROSE) with independent intellectual property rights, and developed four types of automatic warning products for severe convective weather: hail, tornadoes, thunderstorms and gales, and short-lived heavy precipitation. The weather radar mosaic product was upgraded and put into service, achieving national and provincial applications and reducing the product update frequency to six minutes. The high temporal and spatial resolution of weather radar data plays an important role in the development of real-time, kilometer-scale products.

Sea-based
Updated: 22-11-2023
Source: CMA
By the end of 2022, China had built a network of more than five hundred marine observation stations consisting of island stations, offshore platform stations and offshore buoy stations.


Quality Management
Updated: 22-11-2023
Source: CMA
The meteorological observation quality management system, as one of the main internationally prescribed quality management and assurance measurement systems, plays a guiding and standardizing role in the implementation of meteorological observation in China. At present, the quality management system proposed by CMA, which covers the whole process of observation operations, has received ISO9001 certification. The establishment of a quality management system for meteorological observations has provided a strong foundation for meteorological forecasting services and scientific research, thus transforming China from a meteorological service provider of quantity to one of quality.

China Operates REGIONAL SPECIALIZED METEOROLOGICAL CENTER (BEIJING) FOR MARINE METEOROLOGICAL SERVICES
China Maintains WMO Global Data Collection and Processing Center (DCPC)

World Meteriolgoical Cener at Beijing

National Meteorological Centre, China
The National Meteorological Centre (NMC), firstly established as the Central Meteorological Observatory (CMO) in March 1, 1950, is a technology-based non-profit public institution. It is the national weather forecast centre of China, the Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre (RSMC) for Asia designated by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO), and the Environmental Emergency Response Centre (EERC). For more than 60 years, NMC has been dedicating to the improvement of weather forecast accuracy as well as prevention and reduction of natural disasters. So far, a three-level numerical forecast system for medium-term, regional and professional numerical forecast has taken shape.
Forecast and alarm system for typhoon, rainstorm, cold-air outbreak, high temperature, sand and dust storm and heavy fog has been established. NMC is able to make quantitative precipitation forecast for 0 to 3 days, day-by-day rolling element forecast for 4 to 7 days, and extended-range forecasts for 11 to 30 days. A meteorological service system consisting of early warning information service, meteorological service for decision-making, professional meteorological service and specialized meteorological service has been established to provide services covering a wide range of sectors of national economy, including agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, transportation, energy, water, ocean, environmental protection, insurance and commerce.
Main missions:
Taking the lead in designing the weather, ecology and agricultural meteorology systems, carrying out scientific research projects and formulating business codes and criteria; undertaking weather forecast, early warning, monitoring and evaluation across China and major parts of the world; offering meteorological service products on weather, ecology and agriculture to the public; producing comprehensive meteorological service data for the Central Government and relevant authorities to make decisions; developing, improving, upgrading, operating, maintaining, explaining and applying the numerical forecast systems as well as inspecting and evaluating their models; offering technical guidance to subordinating weather forecast stations; and carrying out application researches and R&D in numerical forecast, weather, ecology and agricultural meteorology and other sectors.

China Meteriolgical Research and Development
FENGYUN-3H meteorological satellite successfully launched
Updated: 27-09-2025
Source: China Meteorological News Press
At 3:28 a.m. on September 27, China successfully launched the FENYUN-3H meteorological satellite (FY-3H) using a Long March 4C carrier rocket at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in Gansu. As a new member of the FY polar-orbiting meteorological satellite “afternoon satellite” family, FY-3H payload configuration and performance indicators have reached international sophisticated levels. It will take over the in-orbit operations of the FY-3D, which has been in service for nearly 8 years. While ensuring the core operations of global imaging and atmospheric vertical sounding for polar-orbiting meteorological satellites, it will enhance the data acquisition capability for multiple spheres of the Earth system and further enhancing gobal service capability.

FY-3H was launched. Photoed by REN Changsheng
Dr. CAO Xiaozhong, Chief Commander of the FY Meteorological Satellite Project and Deputy Administrator of the China Meteorological Administration (CMA), stated that in recent years, China has continuously enhanced the influence of its FY meteorological satellites, becoming a role model for serving global sustainable development. After the successful launch of FY-3H, it will continue to give play to the overall advantages of China’s four near-earth orbit observation systems for FY meteorological satellites, further ramp up the capabilities for refined observation of the global atmosphere and the Earth system, and better leverage the application benefits of meteorological satellites in various fields.
WANG Jingsong, Director General of the National Satellite Meteorological Centre (National Space Weather Monitoring and Warning Centre) of CMA and Chief Designer of the FY Meteorological Satellite Project, stated that China adopts a multi-satellite network for near-earth orbit meteorological satellites to obtain observational data completely distributed at the global spatial and temperal and scale. FY-3H will undertake the monitoring mission of “afternoon satellite” and conduct networked observations with the in-orbit FY-3F, FY-3E, and FY-3G. This will provide solid data product support for core meteorological operations with a more stable and higher-quality operational status.
FY-3H is equipped with 9 effective payloads which are of international advanced levels in terms of configuration and performance indicators. These payloads include a newly developed Greenhouse-gases Absorption Spectrometer II (GAS-II), an upgraded Wide-field Auroral Imager-II (WAI-II), as well as 7 inherited payloads such as Medium Resolution Spectral Imager-III (MERSI-III), and Hyperspectral Infrared Atmospheric Sounder-II (HIRAS-II).
GAS-II is the first in the world to achieve global greenhouse gas monitoring with a 100-kilometer swath width.Through refined sounding of atmospheric absorption lines across 4 spectral bands from near-infrared to shortwave infrared, it can obtain column concentration data of major greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, enabling high-precision global greenhouse gas detection and strongly underpin global climate change monitoring and the achievement of “dual carbon” goals.
WAI-II is capable of wide-field Auroral Imaging and sounding of the concentration of precipitating particles. With a spectral coverage of 140nm to 180nm, it can provide real-time forecasts of aurora intensity and extent, as well as current reports on precipitating particles in polar regions, enabling forecasts of magnetic storms, magnetospheric substorms, and polar ionospheric weather.
After FY-3H is put into operation, it will deliver 70 products across 6 major categories, including cloud radiation, sea surface, land surface, atmospheric parameters, atmospheric composition, and space weather. These products will support core meteorological operations, cater to the needs of space weather forecasting and support services, and enhance China’s capabilities in global numerical weather prediction (NWP), g
lobal climate change monitoring, ecological environment monitoring, and disaster prevention and mitigation.
So far, China has launched 22 FY meteorological satellites, with 9 currently in orbit. These satellites continuously deliver data products and services to 133 countries and territories around the world, propping up China’s solution for the United Nations’ Early Warnings for All.
Editor:LIU Shuqiao
China launches meteorological satellite
Fengyun-3 08, together with 2 other satellites, to expand meteorological forecasting, enhance disaster monitoring by providing complete global observational coverage
Saadet Gökce |27.09.2025 – Update : 28.09.2025
 File Photo
File Photo
ISTANBUL
China on Saturday launched a new Fengyun meteorological satellite from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in northwestern Gansu province, according to the state-run CGTN news channel.
The Fengyun-3 08 satellite was carried aboard a Long March-4C rocket to orbit at 3.28 am (1928GMT Friday).
The satellite will be largely utilized for weather forecasting, atmospheric chemistry, and climate change monitoring while it operates in a sun-synchronous orbit.
Fengyun-3 08 is equipped with nine remote sensing instruments, including a medium-resolution spectral imager, an infrared hyperspectral atmospheric detector, and a microwave imager, allowing for precise global monitoring of greenhouse gases over a 100-kilometer (62-mile) width.
Together with two other Fengyun satellites, it will form a network that will provide complete global observation coverage.
This new network will reduce the interval for updating weather data for numerical weather forecasting assimilation from 6 to 4 hours, extend the weather forecast timeline by approximately 24 hours, and nearly double disaster monitoring efficiency.
This is the 596th flight mission of the Long March carrier rocket series.